
When there is a diameter noted to be less than 12mm, this is considered significant for spinal stenosis. The average diameter of a lumbar spinal cord is usually greater than or equal to 15mm. When there is a diameter noted to be less than 10mm, this is considered significant for cervical spinal stenosis. The average diameter of a cervical spinal cord is usually greater than or equal to 13mm. In spinal stenosis, the anteroposterior diameter of the spinal canal is very significant. This condition refers to compression on the spinal cord that is often associated with clumsiness in hands and gait imbalance. Ĭervical stenosis can also progress to myelopathy. Often spinal stenosis is associated with neurologic claudication this refers to the intermittent compression of the lumbar nerve roots resulting in sporadic leg pain. The reason for this is that during sitting, the diameter of the spinal canal increases because of the flexion that occurs. They may report that the pain is worse with standing or walking for prolonged periods and relieved with sitting. If the patient is coming with lumbar stenosis, they will complain of dull achy pain in the legs, calves, thighs, and buttocks area. If it involves the cervical spine, the patient will complain of neck pain that radiates to one or both of their upper extremities. In clinical practice, the physician will encounter patients who complain of pain, numbness, or weakness. Spinal stenosis is most frequently acquired and, therefore, often seen in the geriatric population though it can also be congenital. Spinal stenosis can lead to impingement of the spinal cord, cauda equina, and/or nerve roots. Studies have reported an incidence of 1 in 100 000 for cervical spine stenosis and 5 in 100 000 for lumbar spine stenosis. Spinal stenosis most commonly occurs in the lumbar spine than the cervical spine. The narrowing can compress on nerve tissue that travels through the spine and cause pain, often in the lower back or neck. Spinal stenosis refers to a narrowing of the vertebral canal, which can occur at any level.
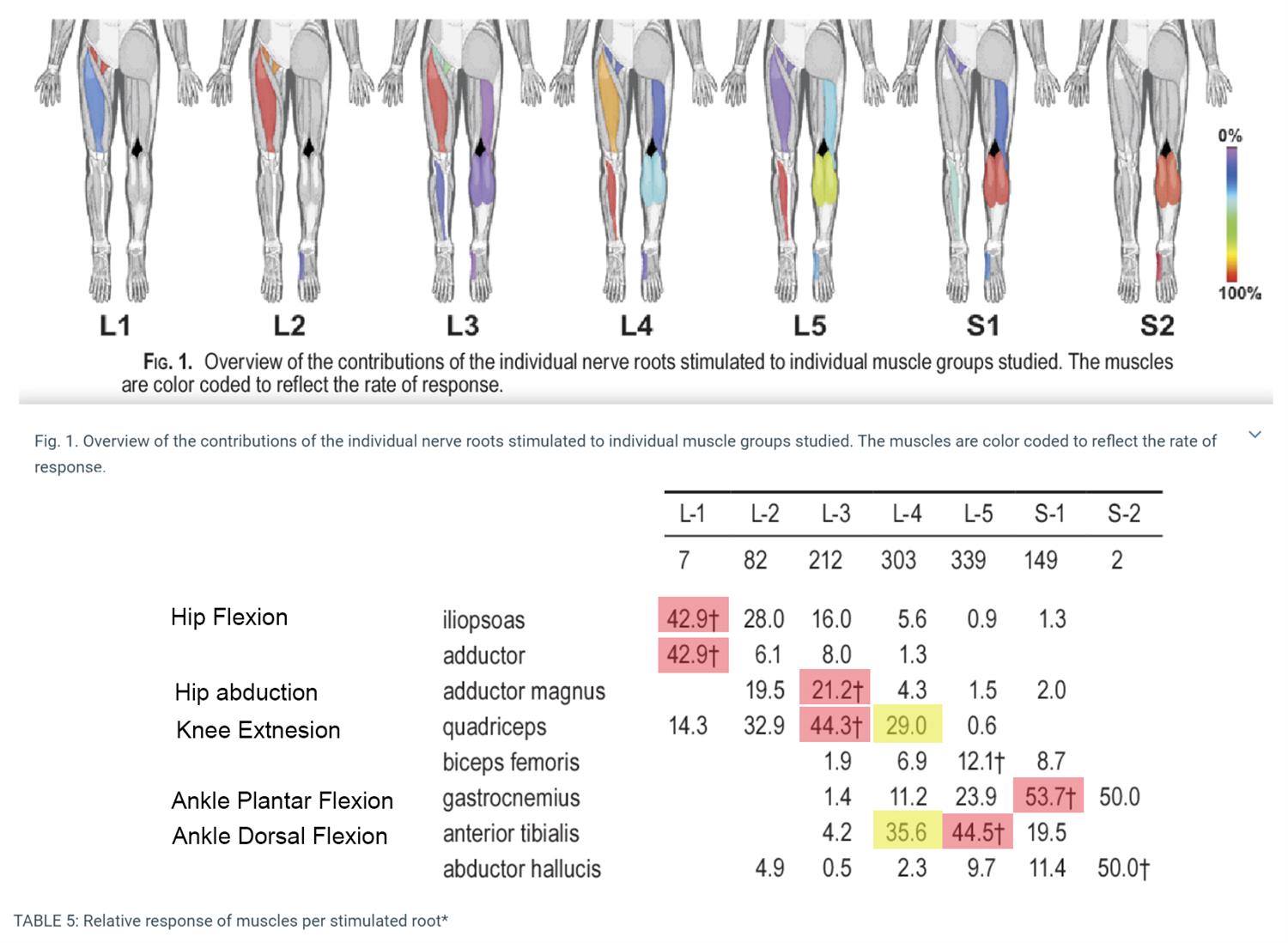
Electrodiagnostic studies are performed especially in spinal stenosis because it helps the clinician to exactly localize and rule out other differentials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
